The Individual Features
Shape Points
- The shape lines form a closed polyline through the shape points.
- Any number of shape points can be added to the polyline.
- The shape points can be added symmetrically to the vertical symmetry axis, which is positioned centered on the base line.

Marking Points

- Are not bound to the shape line string
- You can add any number of marking points.
- The marking points can be added symmetrically to the vertical symmetry axis, which is positioned upright in the center of the base line.
Measures
- Dimensions are length values with names
- They correspond to a variable with a name and are organized in a table.
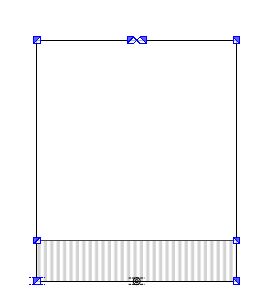
- A dimension can be used horizontally and vertically.
- You can use only one direction of the measure within one fabric piece.
- You can use a measure in both directions within one fabric piece by a formula.
- Dimension types:
- Independent, direct dimensions:
The value does not change within one size.
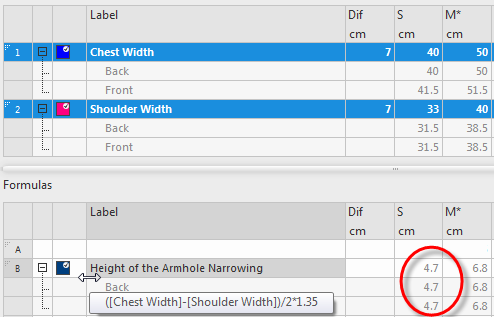
- Dependent, indirect dimensions (formulas):
Are calculated via a formula consisting of direct and indirect dimensions within one size.
e.g. Height is 1.2 * width
- separate tables for dimensions and formulas
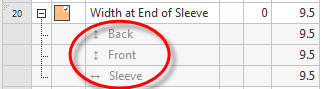
- Sub-rows under the corresponding dimension display the use in the fabric piece.
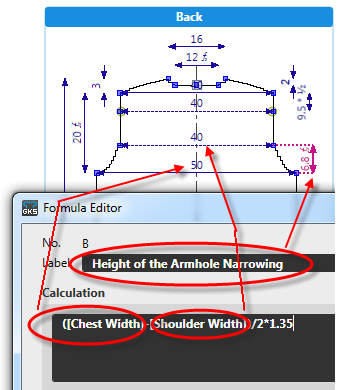
Formulas
- The formulas describe the dependencies of the dimensions within a size.
- The formulas determine dimensions that depend on direct or indirect dimensions and mathematical functions.
Dimensionings
- Initially, a shape or a marking point have a pre-assigned x and y coordinate (in cm or inches), which results from the position drawn in.
The point is freely movable.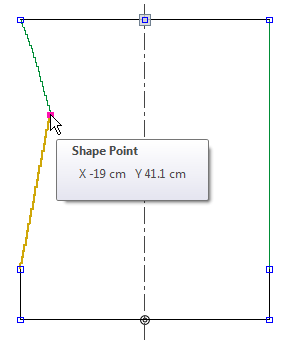
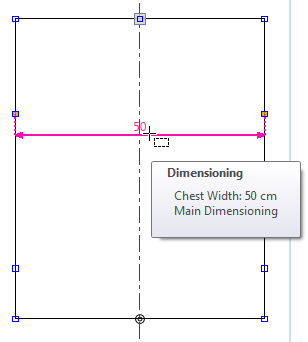
- If a dimension from the table is assigned horizontally or vertically between two points (Dimensioning) the horizontal or vertical position of the points adapts to the set dimension. The point can only be shifted in with limitations.
- Symmetrical points commonly react on a dimensioning.
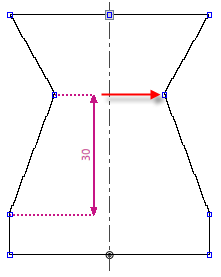
- A dimensioning is the concrete use of a measure between two points of a fabric piece.
- The use of a dimension is entered once per fabric piece as a sub-row in the Measure Table.

- If the value of an independent dimension or the formula of a dependent dimension is changed all dimensions and shape point positions will be newly calculated to meet the new dimension value.
Correction Values
- A constant correction value can be assigned to every dimensioning in use, whether they are independent or dependent.
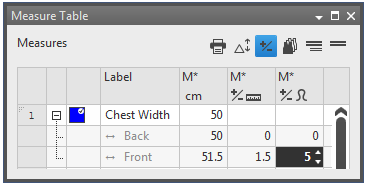
- For example 5 stitches as seam allowance without distorting the actual measure.

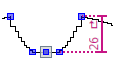
Control Dimensioning
- Between two desired points a control dimensioning can be inserted with horizontal and vertical orientation.
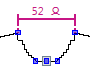
- Horizontal control dimensionings show the number of wales between the points.
- Vertical control dimensionings show the number of stitch rows between the points.
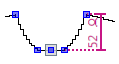
- Vertical control dimensionings show the number of courses between the points.
 What's About Hand Knitting?
What's About Hand Knitting? - The control dimensionings serve for controlling the dimensional accuracy of the fabric.
Grading
- The grading definitions determine the modification of an independent measure switching from one size to the next.


- The formulas of the depending measures describe the dependencies of the dimensions within a size.
- Depending measures switch from one size to the other due to their basic independent measures.
- Step by step from one size to the other:
- Absolute:
A fix value will be added or subtracted to each measure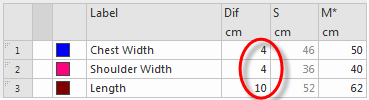
- By Percent:
Every dimension will calculated as a percentage of the preceding size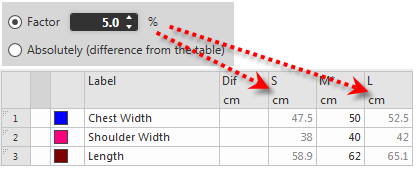
Knitting Areas
- An area with knitting mode can be assigned to every point (shape point or marking point), where it starts in the pattern.
- Areas can be defined as knitting range with:
- Color for stripes and sequence of stripes
- Needle action for simple structures
- Stitch Length
- Stitch Density
- The knitting range overwrites the basic pattern in this area.
- The complete shape width determines the width of the stripe.
- A value can be specified as height of the stripe.
This value can be either a fixed value, an independent or a dependent dimension.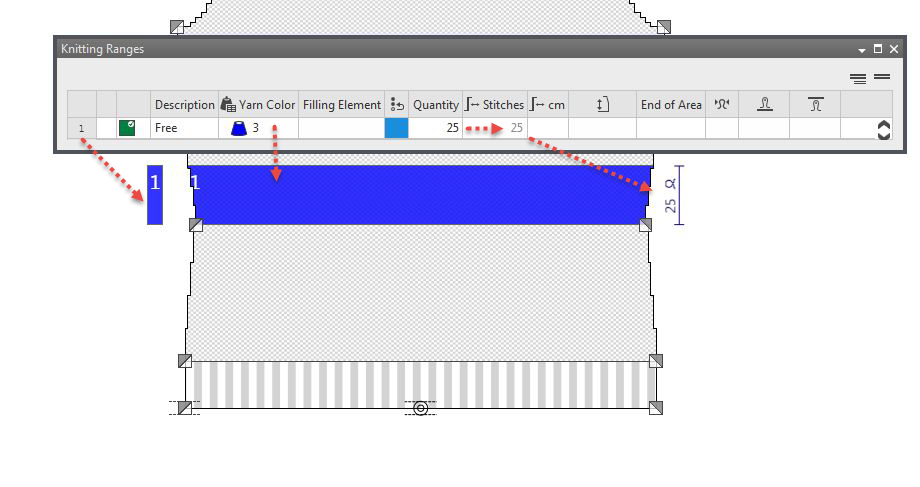
- A fixed value in relation to the height of the reference point can be specified as height position of the stripe.
- For colored stripes the area can be divided into a sequence of sub-stripes.
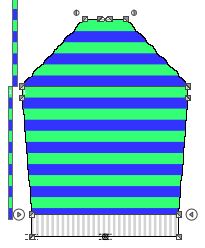
- The color areas can easily be filled with modules and pattern elements on the M1plus via find and replace.
Marking Attributes

- You can add properties to marking points
- Marking modules
- Extention to the left or to the right
Line Attributes
- You can add properties to each line which will be applied to pattern along with it.
- Possible properties:
- Raster properties
(stepping, curve profile, ...) - Functions
(widening, narrowing, fade-out, ...) - Line-bound Markings
(with knitting elements) - Special Behavior
(area for start (rib), filled neckline)
 More about Basics:
More about Basics: